Looking for a Stronger Foundation of Website/Internet Knowledge? A Great Place to Start is With the Difference Between DNS, Domain and Hosting
The internet. We use it every day. It’s become a vital part of our lives. And the funny thing is, not many people know how it all works. From websites to social media, how does this invisible virtual thing work? In this blog, I will take you through some of the basic concepts and methods that help make the internet work in a way that is (hopefully) easy to understand.
I’ll cover everything from servers to the difference between domain and hosting to DNS and how everything works in between. I will use lots of analogies to make this learning process as fun and interesting as possible. Okay then, let’s go ahead and get started.
The Internet Is Like A Virtual City
The easiest way to envision the internet is as a virtual city, and you are a resident in this city. You can communicate to others, go shopping, learn new things and so on. You can even set up a business in this city and sell things. So, here is your starting point, one big virtual city.
The Foundation Is A Wire
A city needs a strong foundation to build upon – something that makes it all work. The internet’s foundation is a wire buried under the ground. Yeah, it’s that simple. This wire could be copper or fiber optics or beamed at satellites or through cell phone networks. This wire serves as the foundation that allows for users (or residents of this city) to build, communicate and do all the things they need to, to keep their city moving.
Servers Are Like Skyscrapers
Servers are these huge special computers that contain and provide information for other computers. They are the skyscrapers of our virtual city. Skyscrapers can hold residential housing, private offices and public malls all the in the same building. It can just do more than what a small building can do, just like how a server can do far more for than our home computers/laptops (which are known as “clients”).
Servers can hold all sorts of data and information, including the files to a website. So, when you visit a website from your computer (aka client), you are really visiting a server that is holding that website (we’ll get back to servers and how their place in our virtual city works).
The Internet Needs Addresses, Too
A city needs addresses, right? Whether it is your home address or a PO box, you need to know how to get to places and where to send things. The internet protocol addresses, more commonly referred to as an IP address, are the mailing addresses of the internet. Every device that connects directly or indirectly to the internet has an IP address. This way, every computer has a way to identify and find other computers.
IP addresses look something like this: 314.37.84.178. Not really a fun way to find other computers or the websites they store. Therefore, we give them domain names (which we’ll dig into more a bit later). So, when you visit ESPN.com, you are really going to the IP Address of the server that hold the files to “ESPN.com.”
In the context of our city analogy, you can think of the domain names as the name of your local business. You don’t want people saying “Hey there is this great restaurant called 445522 Whatever Street, Suite 55.” Doesn’t really ring a bell. But if they say, “Hey let’s check out the Pasta Palace,” now you got me listening.
Domain names serve the same purposes for IP addresses as business names do for building addresses.
The Taxi Drivers
So, we’ve got the internet, which is this underground wire that allows for information to travel and be found. And when you are on the internet your computer is communicating with these servers that host websites through said wire. And the server and client are able to find each other cause they both have IP addresses, but the servers that are holding the website files are being found through a domain name that is a more catchy marketing name instead of the lengthy IP address…
Have I lost you, yet? Hopefully not. These are some of the main components of the internet or “the virtual city.” But were not done. So, let’s say a computer and server are far away and the communication or information being moved can’t make it there. What do you do when you’re in a city and can’t make it to your destination? You call a taxi.
The taxi drivers in this virtual city are called routers. They move “packets,” which are smaller pieces of information that make up the content that is moving through the internet. Routers would be placed where two or more parts of the internet cross (which makes them like traffic signals in a way as well). Routers help the packets move through the internet to reach their destination.
Just like a taxi or delivery drivers help move people or things through a city.
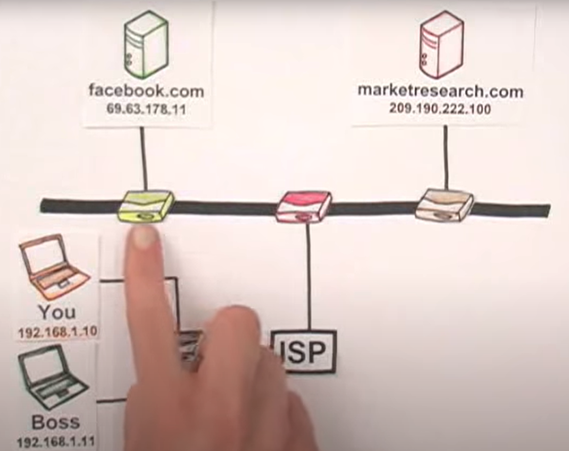
You can see this laid out nicely in the screenshot below, which was taken from a great video about how the internet works. In the screenshot, the finger is pointing to a depiction of a router placed between a web server, ISP and eventually the client.
The Difference Between Domains, Hosting and DNS
The next step to understanding the internet would be to look at things from more of a website level, and a good place to start is with the difference between domains, hosting and DNS.
Domain Names Are the LLCs of the Virtual City
I touched on domain names earlier (and we are back to them, as promised). As we talked about, domain names are sort of the business front name of the IP address. And just like you need to register an LLC (or another business structure) with your state, you need to get your domain name from the city hall of our virtual internet city – domain registrars!
Some of the more popular domain registrars would be Namecheap or GoDaddy. When you buy a domain name, they are typically very affordable, and you’ll pay annually for them.
DNS Servers Are Like Direction Signs
The domain name server (DNS) acts as the directional signs of our virtual city. It has a few elements, namely an A Record and MX Record. The A record directs traffic to your website and the MX record directs traffic to your email. Basically, it points users to the right place – just like direction signs.
Web Hosting Companies Are Like Landlords
Remember servers? The special computers that hold and deliver information – the skyscrapers of our virtual city. Of course, you do. Basically, for your website to be accessible to the public 24/7, it needs to be on a server. Now, having you own server would be an incredible hassle. So, that is when a web hosts come in.
A web host stores all of the physical files of your website on a server in a database somewhere and the server is on 24/7 so users can always access your website. This is so DNS has somewhere to point the user when they are looking for your website, and it points them to your web host. In addition to your website, a web host can host your DNS, domain name and provide email hosting. Therefore, you can get all your hosting done in a single place.
And in the context of our virtual city, the web host is a lot like a landlord. You got your LLC (domain name), you need a place to set up shop (your website) and the landlord (web host) charges you to set up shop in their skyscraper (their web server).
So, when you take a step back and look at how it all works – you would type in a domain name (look for a business), then the DNS A record will point you to the correct place (the direction signs show you where to go) and then you ultimately end up on the web host server (where the business is located).
Recap
I hope this gave you a bit of a different viewpoint on how the internet works – in the context of our virtual city. We’ll be back with more pieces like this where we take deeper dives into the internet, website management and more. Here is a bit of a recap on what we learned.
- The internet is one big virtual city.
- The foundation of this city is the underground wires (or satellites) that make the foundation/architecture which allows for everything to take place in the city.
- IP addresses are the mailing or home addresses of the city.
- Routers are the delivery drivers of the city, moving things (information/content) along.
- Domain names are the LLCs of the city, allowing for businesses to have a name that acts as a front for the IP addresses.
- DNS is the direction signs of the city – moving web traffic to the correct places.
- And web hosts are the landlords of our city – they allow you to set up your website in their servers so users (customers) can visit your site at all times of the day.





